Introduction of Diabetes
In today’s fast-paced world, the prevalence of diabetes has surged, making it essential to comprehend this chronic condition. Diabetes affects millions worldwide, disrupting lives and demanding attention. This blog aims to provide a clear and concise understanding of diabetes, its various types, symptoms, and effective management strategies.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is categorized into three primary types: Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes. Each type has distinct characteristics and triggers.
- Type 1 Diabetes: This autoimmune condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. As a result, the body cannot produce enough insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels. It often develops in childhood or adolescence and requires daily insulin injections.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form, Type 2 diabetes, usually develops later in life due to a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. In this type, the body becomes resistant to insulin, and the pancreas struggles to produce sufficient insulin to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Gestational Diabetes: This type affects pregnant women, causing elevated blood sugar levels during pregnancy. While it typically resolves after childbirth, it raises the risk of Type 2 diabetes development later in life.
Symptoms and Early Detection
Recognizing the symptoms of diabetes is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. Common symptoms include excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, increased hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow wound healing. If these symptoms persist, seeking medical advice is imperative.
Diabetes Management
Managing diabetes is a combination of medication, lifestyle adjustments, and regular medical check-ups.
- Medication: Type 1 diabetes necessitates daily insulin injections or the use of insulin pumps to regulate blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes management may involve oral medications, injectable medications, or insulin therapy, depending on the severity.
- Diet: Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables is essential. Monitoring carbohydrate intake and avoiding sugary snacks helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise enhances insulin sensitivity and helps manage weight, a critical factor in Type 2 diabetes. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity weekly, combined with strength training.
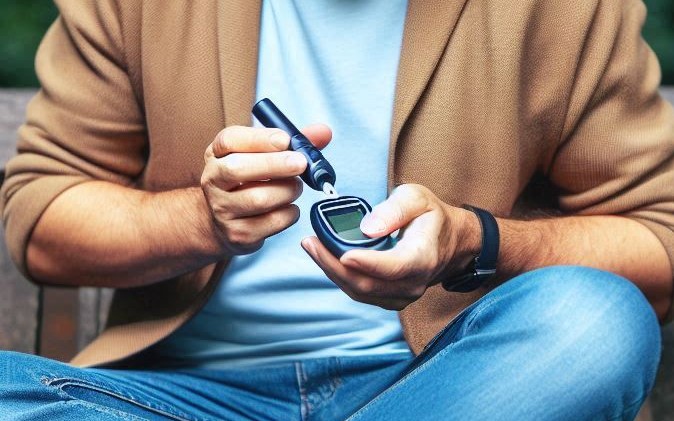
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels helps track fluctuations and enables timely adjustments to medication and lifestyle.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can impact blood sugar levels. Practicing relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can aid in stress reduction.
- Regular Check-ups: Scheduled visits to healthcare professionals assist in tracking the progression of the condition and making necessary adaptations to the treatment plan.
Prevention
While Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, Type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes risk can be minimized through lifestyle modifications:
- Healthy Eating: Opt for whole, unprocessed foods and control portion sizes to maintain a healthy weight.
- Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise to control weight and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of Type 2 diabetes. Even a modest weight loss can have a significant impact.
- Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Control: Keeping blood pressure and cholesterol levels in check lowers the risk of complications.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a serious condition that requires consistent attention and management. By understanding the types, symptoms, and effective strategies for prevention and management, individuals can lead fulfilling lives despite their diagnosis. With a combination of medical care, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing self-monitoring, it’s possible to navigate the challenges of diabetes and maintain optimal health.
Read More: